Olares installation breakdown
This document explains the Olares installation process from the perspective of its four main phases. It is aimed at developers and system administrators who want to understand the installation in detail, including the underlying commands, configurations, and logic behind each phase.
Four phases of installation
The Olares installation process is divided into four phases, each ensuring a smooth and stable setup:
- Precheck: Verifies that the system environment meets all prerequisites for Olares installation.
- Download: Retrieves all necessary files, dependencies, and container images for the installation.
- Prepare: Configures the operating system and system services to create an environment ready for Kubernetes and Olares components.
- Install: Deploys Kubernetes, integrates KubeSphere, and installs core Olares services and applications.
Precheck phase
The precheck phase focuses on verifying that your system meets the necessary requirements for installing Olares. The olares-cli olares precheck command is used to run a series of validation checks. Any issues identified during this phase must be resolved before continuing with the installation.
Key checks include:
- Checks the compatibility with the operating system type, version, and CPU architecture
- Confirms that the system uses
Systemdas its initialization process - Ensures required ports that Olares needs to expose are available
- Verifies that no conflicting container runtime is installed
If the precheck fails, you'll see a warning like this:
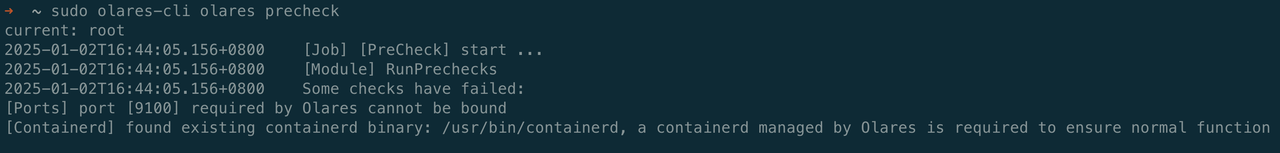
In this example:
- Port
9100required by Olares is already in use. - An existing container runtime is detected in the system.
You must resolve these issues before proceeding.
Download phase
The download phase retrieves the necessary wizard files, system dependencies, and container images required for Olares installation.
Download the wizard file
The wizard file is a metadata package that contains download URLs and configuration details for all Olares components. It is the first file retrieved during this phase, as it provides critical information for the subsequent downloads.
By default, the wizard file is stored in:
HOME/.olares/versions/<version>
where:
$HOME/.olaresis the base directory for Olares.<version>refers to the version number of Olares (e.g.1.12.0-20241215).
Example script output
➜ ~ ./install.sh
the KUBE_TYPE env var is not set, defaulting to "k3s"
olares-cli already installed and is the expected version
downloading installation wizard...
current: root
2024-12-17T18:01:19.501+0800 [Job] [Download Installation Wizard] start ...
2024-12-17T18:01:19.501+0800 [Module] GreetingsModule
Greetings, Olares
2024-12-17T18:01:19.502+0800 [A] ubuntu: Greetings success (611.77µs)
2024-12-17T18:01:19.502+0800 [Module] DownloadInstallWizard
/home/keven/.olares/versions/v1.12.0-20241215/.env
/home/keven/.olares/versions/v1.12.0-20241215/wizard/config/account/Chart.yamlDownload components and container images
Once the wizard file has been downloaded, the script retrieves all necessary dependencies and container images. These files are stored in:
$HOME/.olares/pkgfor dependency packages.$HOME/.olares/imagefor container images.
This storage structure allows reusing stable components across multiple versions to avoid redundant downloads.
Example script output
downloading installation packages...
current: root
2024-12-17T19:41:36.847+0800 [Job] [Download Installation Package] start ...
2024-12-17T19:41:36.847+0800 [Module] GreetingsModule
Greetings, Olares
2024-12-17T19:41:36.848+0800 [A] ubuntu: Greetings success (512.711µs)
2024-12-17T19:41:36.848+0800 [Module] GenerateOlaresUninstallScript
2024-12-17T19:41:36.879+0800 [A] LocalHost: GenerateOlaresUninstallScript success (31.279866ms)
2024-12-17T19:41:36.879+0800 [Module] PackageDownloadModule
2024-12-17T19:41:36.879+0800 checking local cache ...
2024-12-17T19:41:44.614+0800 5 out of 177 files need to be downloaded
2024-12-17T19:41:44.615+0800 (1/5) downloading package olaresd, file: olaresd-v0.0.50.tar.gz
2024-12-17T19:41:51.814+0800 (2/5) downloading image calico/kube-controllers:v3.23.2, file: 521564c4b60ae73c78899b7b40ae655e.tar.gz
...Prepare phase
The prepare phase configures the system environment to support Kubernetes, container images, and Olares services.
This phase involves three main tasks:
- Configure the system
- Set up the container runtime
- Install the system daemon
Configure system
The installation script configures the Linux environment to meet Olares' requirements. These configurations include:
- Adjusts DNS, NTP, and SSH services to ensure proper network functionality and time synchronization.
- Installs essential dependencies (e.g., curl, net-tools, gcc, make) via
apt.
Example script output
preparing installation environment...
current: root
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [Job] [Prepare the System Environment] start ...
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [Module] PreCheckOs
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [A] LocalHost: PreCheckSupport success (29.999µs)
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [A] LocalHost: PreCheckPortsBindable success (144.035µs)
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [A] LocalHost: PreCheckNoConflictingContainerd success (31.009µs)
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [A] ubuntu: PatchAppArmor skipped (7.677µs)
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [A] ubuntu: RaspbianCheck success (5.796µs)
2024-12-17T19:46:39.517+0800 [A] ubuntu: CorrectHostname success (5.363µs)
nameserver
nameserver
2024-12-17T19:46:41.921+0800 [A] ubuntu: DisableLocalDNS success (2.40336625s)
2024-12-17T19:46:41.921+0800 [INFO] installing and configuring OS dependencies ...
2024-12-17T19:46:41.921+0800 [Module] InstallDeps
Hit:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease
Hit:2 https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Hit:3 http://hk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease
...Set up container runtime
The container runtime is a critical component for running containerized applications. During this step, the installation script:
- Installs and start the previously downloaded dependencies
- Installs containerd on the system and start the service
- Imports the downloaded container images into containerd
Example script output
2024-12-17T19:47:37.510+0800 [Module] InstallContainerModule(k3s)
2024-12-17T19:47:37.518+0800 [A] ubuntu: ZfsMountReset skipped (7.321811ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:37.525+0800 [A] ubuntu: CreateZfsMount skipped (7.322591ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.188+0800 [A] ubuntu: SyncContainerd success (662.643982ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.368+0800 [A] ubuntu: SyncCrictlBinaries success (179.758334ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.399+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateContainerdService success (31.410118ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.451+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateContainerdConfig success (52.047108ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.505+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateCrictlConfig success (53.760209ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.857+0800 [A] ubuntu: EnableContainerd success (352.128078ms)
2024-12-17T19:47:38.857+0800 [Module] PreloadImages
2024-12-17T19:47:41.665+0800 (1/145) imported image: rancher/mirrored-pause:3.6, time: 194.363948ms
...Install system daemon
The Olares system daemon, olaresd, is then installed and started to monitor the system and automatically perform maintenance tasks.
Example script output
024-12-17T19:52:31.862+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateOlaresdEnv success (23.829684ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:31.862+0800 template OlaresdService result: [Unit]
Description=olaresd
After=network.target
StartLimitIntervalSec=0
[Service]
User=root
EnvironmentFile=/etc/systemd/system/olaresd.service.env
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/olaresd
RestartSec=10s
LimitNOFILE=40000
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
2024-12-17T19:52:31.885+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateOlaresdService success (23.050958ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:32.033+0800 [A] ubuntu: EnableOlaresdService success (147.987242ms)
...Install phase
The install phase brings all system components online and ensures the runtime environment is fully operational.
During this phase, the script primarily completes the following tasks:
- Deploy Kubernetes.
- Integrate KubeSphere for cloud-native management and observability.
- Configure the Olares account.
- Deploy and start built-in apps and services.
Deploy Kubernetes
Kubernetes is the backbone of the Olares system. During this step, the installation script:
- Starts the etcd database.
- Starts and configures K3s.
- Installs a Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin for cluster networking.
- Copies the
kubeconfigfile to the current user's directory, enabling interaction with the cluster viakubectl.
K3s is the default Kubernetes distribution for Olares due to its lightweight design and ease of use. However, kubernetes is also available for advanced or custom setups.
On macOS, the scripts uses minikube, which will skip the above step.
Example script output
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] admin-ubuntu serving cert is signed for DNS names [etcd etcd.kube-system etcd.kube-system.svc etcd.kube-system.svc.cluster.local lb.kubesphere.local localhost ubuntu] and IPs [127.0.0.1 ::1 192.168.1.16]
[certs] member-ubuntu serving cert is signed for DNS names [etcd etcd.kube-system etcd.kube-system.svc etcd.kube-system.svc.cluster.local lb.kubesphere.local localhost ubuntu] and IPs [127.0.0.1 ::1 192.168.1.16]
[certs] node-ubuntu serving cert is signed for DNS names [etcd etcd.kube-system etcd.kube-system.svc etcd.kube-system.svc.cluster.local lb.kubesphere.local localhost ubuntu] and IPs [127.0.0.1 ::1 192.168.1.16]
2024-12-17T19:52:36.957+0800 [A] LocalHost: GenerateETCDCerts success (263.237575ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.263+0800 [A] ubuntu: SyncCertsFile success (306.213676ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.264+0800 [A] ubuntu: SyncCertsFileToMaster skipped (20.351µs)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.264+0800 [Module] InstallETCDBinaryModule
2024-12-17T19:52:37.698+0800 [A] ubuntu: InstallETCDBinary success (434.014395ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.728+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateETCDService success (30.732882ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.728+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateAccessAddress success (23.491µs)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.728+0800 [Module] ETCDConfigureModule
2024-12-17T19:52:37.728+0800 [A] ubuntu: ExistETCDHealthCheck skipped (9.903µs)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.753+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateETCDConfig success (24.125665ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:37.773+0800 [A] ubuntu: AllRefreshETCDConfig success (20.321235ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.048+0800 [A] ubuntu: RestartETCD success (2.274541565s)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.068+0800 [A] ubuntu: AllETCDNodeHealthCheck success (20.251062ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.094+0800 [A] ubuntu: RefreshETCDConfigToExist success (26.207599ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.129+0800 [A] ubuntu: AllETCDNodeHealthCheck success (34.462881ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.129+0800 [Module] ETCDBackupModule
2024-12-17T19:52:40.185+0800 [A] ubuntu: BackupETCD success (56.639923ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.230+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateBackupETCDService success (44.727929ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.273+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateBackupETCDTimer success (42.839457ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.396+0800 [A] ubuntu: EnableBackupETCDService success (122.621074ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:40.396+0800 [Module] InstallKubeBinariesModule
2024-12-17T19:52:41.188+0800 [A] ubuntu: SyncKubeBinary(k3s) success (791.866964ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:41.218+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateK3sKillAllScript success (30.442837ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:41.253+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateK3sUninstallScript success (34.802683ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:41.268+0800 [A] ubuntu: ChmodScript(k3s) success (14.640733ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:41.268+0800 [Module] K3sInitClusterModule
2024-12-17T19:52:41.334+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateK3sService success (66.556896ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:41.379+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateK3sServiceEnv success (44.492752ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:41.414+0800 [A] ubuntu: GenerateK3sRegistryConfig success (34.814475ms)
2024-12-17T19:52:46.511+0800 [A] ubuntu: EnableK3sService success (5.097800474s)
2024-12-17T19:52:46.572+0800 [A] ubuntu: CopyKubeConfig success (60.33887ms)
...Integrate KubeSphere
KubeSphere is installed on top of Kubernetes to enhance system management and observability. It provides features such as:
- System monitoring and alerting.
- Resource and workspace management.
- Namespaces and custom resource definitions (CRDs).
Configure account
The Olares ID is created in the LarePass app. During this step, the installation script prompts you to enter the following info, so you can use LarePass to activate Olares later:
- Olares domain name: Olares provides default names
olares.comandolares.cn. This can be customized if the custom domain has been added to Olares Space. - Olares ID: Enter the username part of your Olares ID.
This creates a system account for logging in to Olares and completes several background access and permission configurations.
Example script output
Enter the domain name ( olares.com by default ):
2024-12-17T20:58:15.690+0800 using Domain Name: olares.com
Enter the Olares ID (which you registered in the LarePass app): marvin113
2024-12-17T20:58:52.584+0800 using Olares Local Name: marvin113
2024-12-17T20:58:52.584+0800 using Olares ID: marvin113@olares.com
2024-12-17T20:58:52.584+0800 using password: 2uO5PZ2XDeploy built-in applications
The final deployment step installs core services and user applications using Helm charts:
- Core system services (in the
os-systemnamespace): Includes backups (Velero), storage (OpenEBS), Redis, Nats, MinIO, etc. - User applications (in namespaces like
user-space-xxx): Includes Files, Desktop, Settings, etc.
During installation, the log will display messages such as [helm] app installed success and xxx created, indicating that the respective Helm charts or Kubernetes resources have been installed successfully.
Example script output
2024-12-17T19:53:18.382+0800 [A] ubuntu: InitKsNamespace success (2.678362348s)
2024-12-17T19:53:18.382+0800 [Module] DeploySnapshotController
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/volumesnapshotclasses.snapshot.storage.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/volumesnapshotcontents.snapshot.storage.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/volumesnapshots.snapshot.storage.k8s.io created
2024-12-17T19:53:18.924+0800 [helm] app installed success {"NAME": "snapshot-controller", "LAST DEPLOYED": "Tue Dec 17 19:53:18 2024", "NAMESPACE": "kube-system", "STATUS": "deployed", "REVISION": 1}
2024-12-17T19:53:18.924+0800 [A] ubuntu: CreateSnapshotController success (541.656132ms)
2024-12-17T19:53:18.924+0800 [Module] DeployRedis
secret/redis-secret created
2024-12-17T19:53:19.057+0800 [A] ubuntu: CreateRedisSecret success (133.123121ms)
2024-12-17T19:53:19.189+0800 [A] ubuntu: BackupRedisManifests success (132.045425ms)
2024-12-17T19:53:19.339+0800 [A] ubuntu: DeployRedisHA success (149.251633ms)
local (default) openebs.io/local Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 31s
local (default) openebs.io/local Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 31s
2024-12-17T19:53:19.971+0800 [helm] app installed success {"NAME": "redis", "LAST DEPLOYED": "Tue Dec 17 19:53:19 2024", "NAMESPACE": "kubesphere-system", "STATUS": "deployed", "REVISION": 1}
...Complete the installation
Once all components are deployed, the script outputs a summary with a URL for the activation wizard:
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 [INFO] Installation wizard is complete
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 [INFO] All done
------------------------------------------------
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 Olares is running at:
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 http://192.168.1.16:30180
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 Open your browser and visit the above address
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 with the following credentials:
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 Username: marvin113
2024-12-17T21:00:58.086+0800 Password: 2uO5PZ2XTo complete the installation, you need to:
- Open your browser and enter the provided URL.
- Log in to the activation wizard with initial password.
- Follow the on-screen prompt to finish the activation.
After activation, your Olares will be fully operational and ready to use.