Olares installation overview
This document provides a high-level overview of the Olares installation process, focusing on its overall architecture and core components. It is intended for system administrators and developers who need a foundational understanding of how Olares operates and is installed.
Three layers of Olares installation
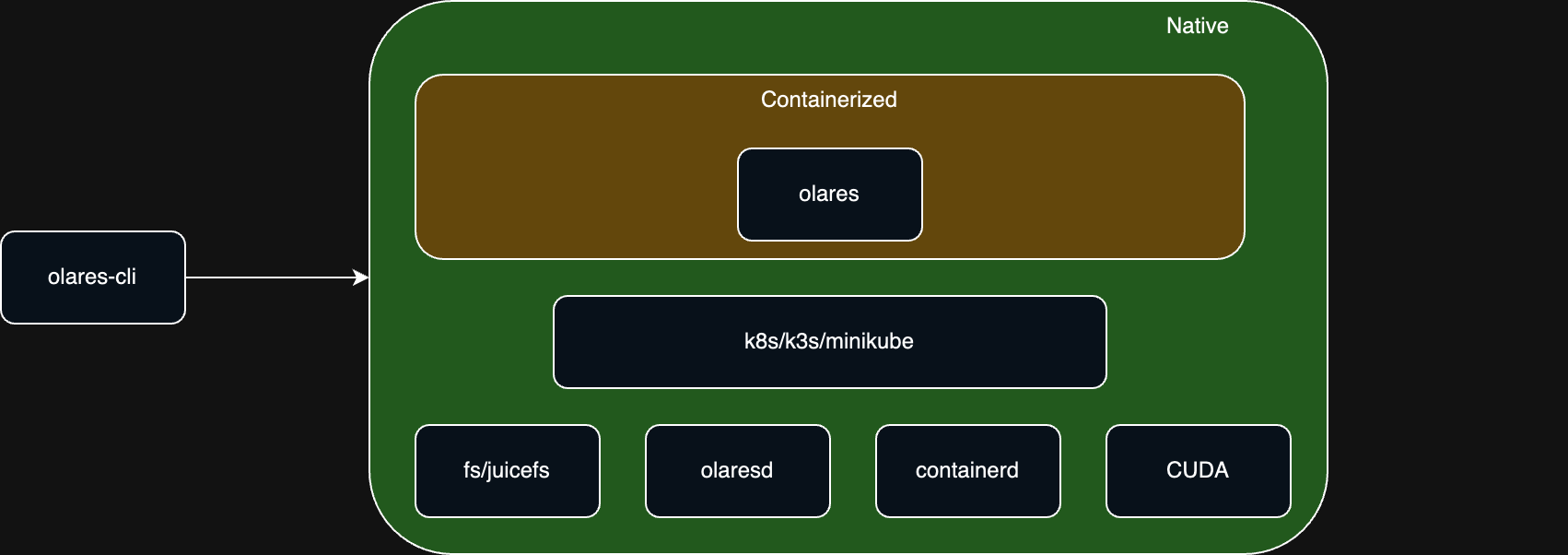
The Olares installation is structured into three key layers:
- Native layer: Manages Linux system configurations and installs essential environment dependencies.
- Container orchestration layer: Deploys the Kubernetes cluster to enable automated service management and scaling.
- Containerization layer: Launches containerized core system services and user applications, providing the final runtime environment.
The installation process is managed by the olares-cli tool. This command-line tool orchestrates the installation, configuration, and lifecycle management of all components.
TIP
To understand the detailed installation process phase-by-phase, refer to Olares installation breakdown.
Native layer
The Olares installation process begins at the native layer, ensuring that the underlying Linux environment supports distributed storage, container runtimes, and Kubernetes cluster management.
This layer's configuration includes core Linux system settings, file system initialization, container runtime installation, and deployment of critical system services.
Environment configuration
The installation first configures the basic Linux installation environment. This includes setting up Domain Name System (DNS), Secure Shell (SSH), and Network Time Protocol (NTP) services to ensure time synchronization and remote management capabilities.
Additionally, necessary dependencies such as the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) and Network Tools (net-tools) are installed to ensure a robust runtime environment.
File system configuration
The root file system (rootfs) is used to store and access system core components and user data. Olares supports the following two file systems based on deployment needs:
LocalFS (default): Uses the local Linux disk for storage. It is ideal for single-node deployments that require high data throughput without the need for network sharing.
JuiceFS: Provides a distributed file system for multi-node cluster. File data are stored in locally installed MinIO instances or remote storage buckets such as Amazon S3. This setup allows different storage nodes to share a unified storage view.
Enable JuiceFS
JuiceFS and MinIO are not installed by default. To enable them, set the necessary environment variables or use
olares-cliwith JuiceFS-specific flags.
Container runtime: containerd
Olares uses containerd, a lightweight container runtime, for containerized deployments. Its features include:
- Container image management:
- Downloads packaged container images from the Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Imports them into containerd during the "prepare" phase
- Starts the images as container processes during the "install" phase
- Container lifecycle management: Starts, stops, restarts, and monitors containerized application services.
Compatibility issue
If containerd is already installed on your machine (for example, as part of Docker), it may cause compatibility issues with the containerd used by Olares. Please uninstall the existing containerd before installing Olares.
System daemon: olaresd
olaresd is the system daemon that runs in the background, providing essential management functionalities such as:
- Automated configuration updates: Automatically adjusts configurations when system changes (e.g. IP changes) are detected.
- Remote system management: Executes remote system operations, such as Olares installation and activation, based on requests issued from the LarePass client or
olares-cli.
CUDA support
To enable GPU acceleration for local AI models and applications, Olares supports automatic installation of the CUDA toolkit and drivers through olares-cli.
Container orchestration layer
The container orchestration layer integrates system components into an efficient runtime environment using Kubernetes.
Roles of Kubernetes
Kubernetes serves as the backbone of the container orchestration layer, providing automated deployment, operation, scaling, and management of multi-component services.
Compared to tools like Docker Compose or Docker Swarm, Kubernetes offers:
- High scalability and production-grade reliability.
- Robust community support and a rich ecosystem for integrating applications via Helm Charts, Operators, and Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs).
Kubernetes options in Olares
Olares supports the following Kubernetes setups:
- K3s (default): A lightweight Kubernetes distribution optimized for resource efficiency on local hardware.
- Kubernetes: The full-featured Kubernetes distribution for advanced or custom deployments.
- minikube (macOS only): A tool that sets up a single-node Kubernetes cluster, ensuring consistent features and user experience.
Containerization layer
The containerization layer is where Olares' components and applications come together to provide the system's full functionality. All Olares components and user applications run within containers, with the full lifecycle managed via Kubernetes. This ensures that the system remains efficient, stable, and scalable.
Once Olares is installed and activated, you can view the running containers through a graphical user interface provided by the Control Hub app:
